What is a DPF?
A DPF is designed to make your diesel car cleaner and prevents any harmful emissions exiting the exhaust system.
The Cazoo editorial team
Published on 19 November 2025 | 1 min read
Diesel vehicles make a lot of sense for buyers covering lots of miles and need a car that is going to be efficient and frugal.
There are thousands of second-hand diesel cars on the market that are practical and can achieve lots of miles, which are all available at Cazoo.
However, all modern diesel vehicles will be fitted with something called a DPF, which sits in the vehicle’s exhaust system to help reduce emissions and make it cleaner and greener.
So, before you go out and buy a second-hand diesel, what does ‘DPF’ stand for? And…what are its positives and negatives? With that in mind, we’ve compiled a handy guide to all the things you need to know about DPFs.
What is a DPF?
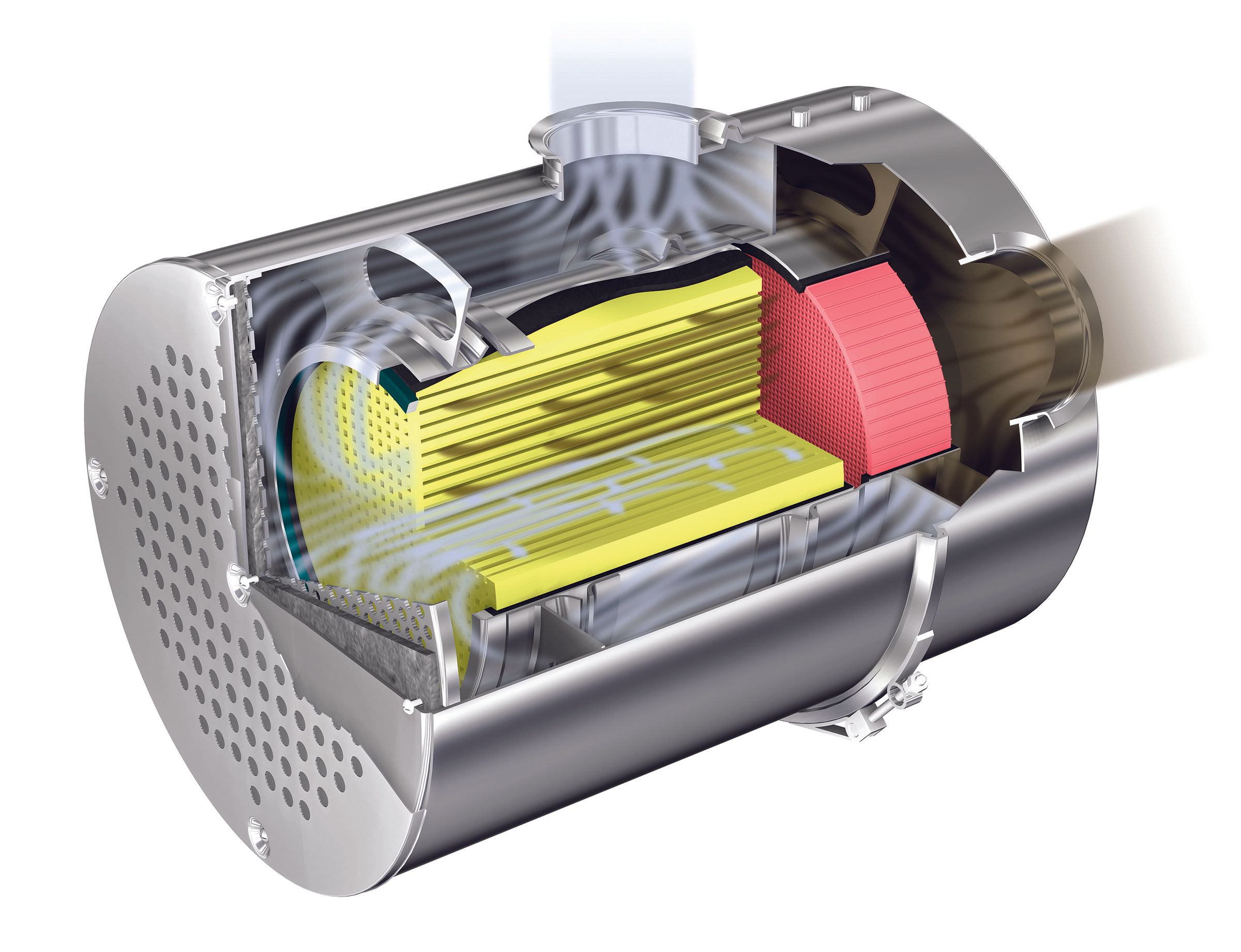
Let’s start with what the acronym stands for. A DPF is short for ‘Diesel Particulate Filter’ and is a device that is stored within a diesel car’s exhaust system.
DPFs have been mandatory on diesel vehicles since September 2009 as part of the Euro Five emissions legislation.
A DPF’s purpose is to capture and store harmful exhaust soot and gases from a diesel car’s exhaust pipe, which helps reduce carbon emissions and makes the car less polluting when driven on public roads.
Search for used diesels on Cazoo
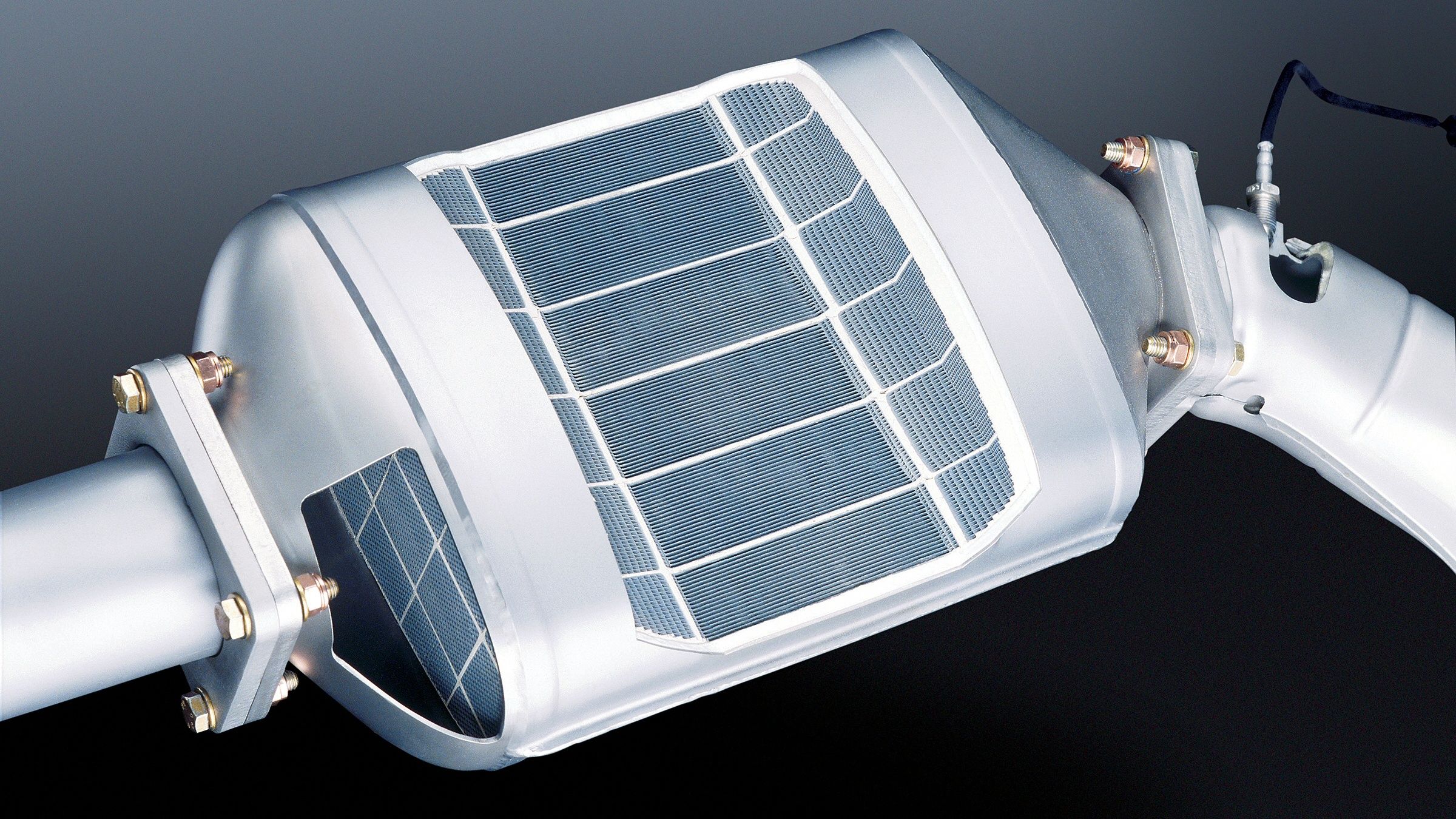


How does it work?
A DPF is constructed using a ceramic honeycomb structure within the device itself, which helps trap harmful soot exiting the exhaust system.
Over time, the soot builds up and is burnt off in the device by a process that is called ‘regeneration’, converting the soot to ash which helps reduce exhaust carbon emissions and makes a diesel vehicle much more cleaner-burning.
Diesel vehicles that are driven regularly and cover lots of miles allow their DPFs to work constantly to help the exhaust gases burn off those dirty soot particulates from exiting the exhaust system and make them run smoothly and efficiently.
What are the benefits?
The benefits to DPFs are that they are designed to eliminate nasty exhaust particulates and soot from going into the atmosphere. This helps improve air quality, especially in cities, it reduces CO2 emissions, which also helps keep vehicle road tax down.
A DPF also helps improve your diesel car’s engine performance and efficiency, while fuel consumption is increased too.
When a diesel vehicle is consistently used, its DPF is regularly cleaned out by the exhaust gases, which enables the engine to run smoothly and helps retain its maximum performance.


What are the negatives?
If you drive a diesel vehicle and don’t do a lot of miles, then you might want to think about switching to a petrol car.
This is because diesel engines are designed to be regularly used and if they’re not, DPFs can get clogged up, which reduces the vehicle’s performance, efficiency and makes them run rough.
A DPF over time will get clogged up from the car’s exhaust soot, because of the restricted exhaust gas flow going into the device. They can also get bunged up from covering short journeys as the engine won’t have enough time to get up to temperature to allow the regeneration cycle to enable exhaust gases to flow into the DPF, which also causes soot build up.
It’s also illegal to remove the DPF from your car if it has one fitted from the factory. This is because the vehicle will be a lot more polluting without it, allowing dirty exhaust gases to enter the atmosphere, causing air pollution. Also, your car will fail its MOT on emissions and owners can face up to £1,000 fines on cars and £2,500 if you own a van.
How much does a new DPF replacement cost?
If a DPF fails or its gets clogged up to the point that it’s damaged, then they can be costly to replace.
Depending on the vehicle and manufacturer of the DPF, prices can vary from £1,000 and £3,500, which in some scenarios can outweigh the total value of the car.
Also, DPFs usually have a life expectancy of between 100,000 miles and 200,000 miles if your car is serviced on time and is not neglected. DPFs will need to be replaced over time, regardless of whether they fail or begin to deteriorate with age.
